Today, we shall discuss the standards, protocols, and standards organizations. There is a difference between standard and protocol. Standards are guidelines, whereas a protocol is a rule. The protocol may satisfy a standard, or it may not; a protocol is an exact definition of how the exchange of information occurs. The standards organization or standards body is one who develops, approves, or maintains those standards. Let’s see one by one what are the Standards, Protocols, and Standards Organizations.
Standards, Protocols, and Standards Organizations: Standards
Standards are open frameworks/rules to guarantee the interoperability between different equipment manufacturers. Or, we can say, they are guidelines or agreed upon ways for doing something to be followed by the vendors, manufacturers, government agencies, etc. to ensure the interconnectivity.
Some of them have a wide implementation, whereas some may not be. Similarly, some standards may be open, and some may be proprietary. The ISO OSI 7 layer model is an example of one of the famous open standards.
MP3 for audio encoding is an example of proprietary, and popular standard.
There are two types of data communication standard:
De facto:- (Pronunciation: dee fak-toh: Origin: Latin) are not officially sanctioned, but adopted by the organizations. For example, the QWERTY keyboard, Microsoft Word DOC format, etc. are the de facto standards.
De jure:- (Pronunciation: “di joo r-ee”: Origin: Latin) Those standards are approved by an officially registered body. The well-known examples of De jure standard HTML, PDF, etc.
Standards, Protocols, and Standards Organizations: Protocols
We need specific protocols to communicate between any two people, machines, or devices. A protocol is defined as a set of rules that governs communication. Or we can say, it’s a detailed plan of the experiment, treatment, or procedure in telecommunication.
There is protocol in daily life like how to greet whom while meeting people, how to respond while picking up the phone, etc.
In a computer network, communication between two different devices of different make and model is possible through a common protocol. The protocol defines how and when to communicate, what is be the mode, speed, encoding, etc. The protocol defines the Syntax, semantics, and the timing for the communication.
In a computer network, communication between two different devices of different make and model is possible through a common protocol. The protocol defines how and when to communicate, what is be the mode, speed, encoding, etc. The protocol defines the Syntax, semantics, and the timing for the communication.
Standards, Protocols, and Standards Organizations: Standards Organizations
ISO (International organization for standardization)
Formed in 1947, ISO is a non-government, independent, international organization. ISO comprises of 164 national standard bodies from various countries worldwide. ISO has about 23k international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. Three types of membership status are there; Member body (or full members), Correspondent members, Subscriber members. The member body of ISO from the United States is ANSI and that from India is BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards).
Out of the popular standards, ISO/IEC 2701- INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT is the standard for security of any kind of Digital information. In 1983, ISO developed the OSI reference model, a 7 layer architecture for computer communication.
International Telecommunications Union–Telecommunications Standards Sector (ITU-T)
Earlier known as Consultative Committee for International Telegraphy and Telephony (CCITT) worked for the research and establishment of the standards in telecommunication. In 1993, it gets the name ITU-T. ITU-T allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, develops the technical standards for the interconnection of networks and technologies.
ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
Its a private, non-profit, non-government organization. Now its a member body of ISO representing the US. Primarily focused in the US, it works for coordination of the US standard with international standards. Its membership comprised of Government agencies, Organizations, Companies, Academic and International bodies, and individuals.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing innovations in technology. IEEE’s membership has been composed of engineers, scientists, and allied professionals since earlier. Apart from its engineering core, IEEE members are also from several other backgrounds like computer scientists, software developers, information technology professionals, physicists, medical doctors, and many others. IEEE develops global standards in almost all fields including Information Technology. Among more than a thousand standards, the IEEE 802 LAN/MAN group of standards is widely used in computer networking which includes 802.3 aka Ethernet, 802.11, aka Wi-FI, etc.
Electronic Industries Alliance/Telecommunication Industry Association (EIA/TIA)
Electronic Industries Alliance(EIA) was known as the Electronic Industries Association until 1997. EIA has developed several electronic signaling information and physical connection interfaces. It ceased operation in 2011. One of the notable standards of EIA is serial communication standard RS 232. Though EIA ceased to function, its function was split into different sectors. One of them is TIA (Telecommunication Industry Association- accredited by ANSI) that developed standards for Information and communication technology (ICT) products. The cabling standard EIA/TIA 568 for 8 wire is now known as ANSI/TIA 568 standard.
ETSI (European Telecommunication Standard Institute)
It is a European standardization organization that is independent, non-profit, and works in the Information and communication technology (ICT) industry. It supports the development and testing of globally applicable ICT enabled systems, services, and applications. ETSI has members from 66 countries/provinces inside and outside of Europe. ETSI is one of the technical bodies of CEN (European Committee for Standardization).
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium)
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is an international community where the member organization and public together work for developing the web standards. Led by its founder (founded in 1994), Tim Berners Lee along the team working together with a mission to ensure that the web is available to all.
Open Mobile Alliance (OMA)
It is a standard organization formed in 2002, that develops open standards for the mobile phone sector. It is a non-government forum that works intending to provide interoperability across countries, operators, and mobile terminals.
Forums
Forums are formed by special interest groups with representatives from concerned corporations. The work with the universities to test, evaluate, and standardize new innovations. The standards organizations take too much time in completing the procedures and standardize the technology. The forums dealing dedicatedly in a particular technology, they speed up and use the technology without waiting for the standards organizations. Forums are basically community standards intending to accelerate the concerned technology innovation and creating standards.
There are various forums to name, some of them are :
- Frame Relay Forum
- ATM forum
- Universal Plug n Play (UPnP) forum
- Broadband Forum (BBF)
The Internet Ecosystem
The Internet Society (ISOC) uses the term The Internet Ecosystem to define all the associated organizations and communities that help the Internet grow and evolve. The resources and documents are available for reading and sharing in the ISOC web site at this link: https://www.internetsociety.org/internet/who-makes-it-work.
The resource is freely available to share under this license: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
The summary of the documents is presented here for easy understanding of readers.
The Internet Ecosystem comprises of:-
- Technical organizations like the IETF, and the W3C, help to coordinate and implement open standards.
- Global and local organizations that manage the addressing capabilities resources like the ICANN, IANA, RIR, Domain name registrars, and registrars.
- Operators, Engineers, and vendors who provide infrastructure services like Domain Name Service providers, Operators, and IXPs*.
- Internet users who use the Internet and help it to grow.
- Educators in various organizations, institutes, etc. who teach people and build capacity for deloping and using Internet technologies.
- Policy and Decision-makers who develop and maintain global and local policies.
*(Internet eXchange Point, is a physical location where all the Internet Service Providers and the Content Delivery Networks connect and exchange Internet traffic.)
Internet Society (ISOC)
It was formed in 1992 by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn, two of the fathers of the Internet. ISOC is a leading non-profit organization that provides Internet standards, access, education, and policy. ISOC is a global cause-driven organization that is governed by different trustees. The motto of the organization is that the Internet remains open, transparent, and available to all. It works in conjunction with all other Internet bodies and coordinates and provides support.
The organization is responsible for promoting the evolution and growth of the global Internet. It consists of individual members, organization members, and chapters. The mission of ISOC is to encourage open development, make the Internet transparent and useful for the people throughout the world.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
IETF, formed in 1986, is a non-profit standards organization for developing Internet standards. But after 1993, it started working as a part of ISOC. It is a large, open, international community involved with the evolution of Internet architecture. The community constituted of network designers, operators, vendors, and researchers. It has a reasonable role in defining the technical foundations for protocols, number resources, and domain names.
Internet Research Task force (IRTF)
In contrast to IETF, which looks after the short term issues of engineering and standard making, the IRTF focuses on longer-term research issues related to the Internet. The research groups associated with IRTF works for topics like Internet protocol, architecture, application, and technology.
IAB (Internet Architecture Board)
It is the advisory body of Internet Society (ISOC) and works as a part of IETF. IAB responsible for oversight of IETF activities, Internet Standards Process oversight and appeal, and the appointment of the RFC Editor and also responsible for the management of the IETF protocol parameter registries.
Regional Internet Registries (RIRs)
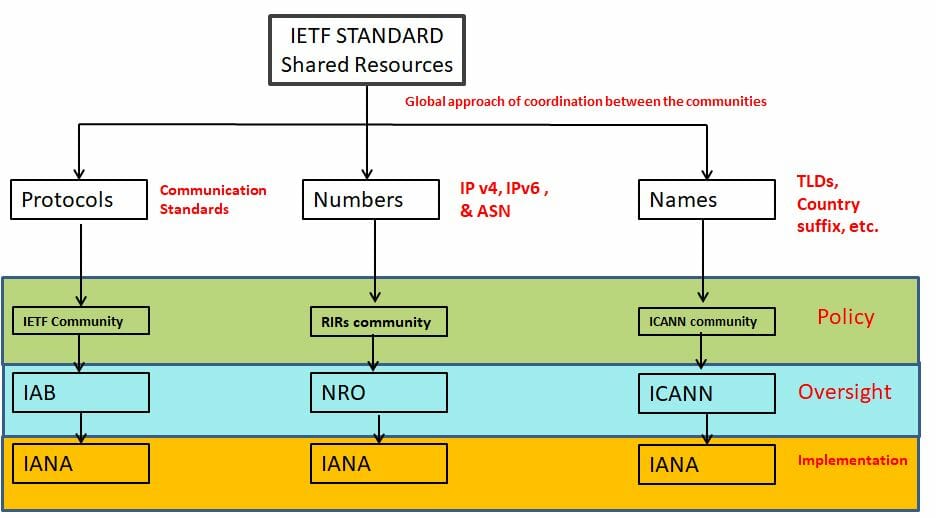
Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) looks after the allocation and registration of Internet number resources among one of the five different regional registries. The Internet number resources include IP address and Autonomous System Number (ASN). It has five regional registries. All five RIRs consists of the Internet community in its region and a member of the Number Resource Organization (NRO).
| Srl Number | RIR | Area |
| 1 | The African Network Information Center (AFRINIC) | Africa |
| 2 | The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) | Antarctica, Canada, parts of the Caribbean, and the United States. |
| 3 | The Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) | East Asia, Oceania, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. |
| 4 | The Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre (LACNIC) | most of the Caribbean and all of Latin America. |
| 5 | The Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (RIPE) | Europe, Central Asia, Russia, and West Asia. |
The Number Resource Organization (NRO)
The Number Resource Organization (NRO) is a coordinating body for the five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) that manage the allocation of Internet number resources including IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and ASNs. The NRO exists to preserve the unassigned Number Resource pool, to support and protect the bottom-up policy development process, and to function as a focal point for community input into the RIR system.
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers)
ICANN is a non-profit organization maintaining the database related to the Internet name resource as well as number resources. Formed in 1998, ICANN is an American multi-stakeholders group. It is responsible for the works related to namespaces like the policy development for internationalization of DNS systems, the introduction of new TLDs, and the functions of root name servers. The ICANN assigns the IPv4 and IPv6 blocks to RIRs, and also maintains registries of Internet Protocol identifiers.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
IANA is responsible for regulating some of the key components that keep the Internet running smoothly. Though the Internet is called worldwide network free from central coordination, there is a technical need for some key parts of the Internet to be globally organized, that role is done by IANA. It allocates a unique code and numbering system to Internet protocols.
The function of IANA mainly consists of management of DNS root, Coordination of global pool of IP and ASN numbers, and management of Internet Protocols numbering system. Today those services are provided by Public Technical Identifiers (PTI) an affiliate of ICANN. Since 2016, PTI is responsible for the operation of IANA functions on behalf of ICANN.
IANA does not directly set policy to operate, instead, they implement agreed policies and principles neutrally and responsibly. In the above diagram, you can see that IANA is at the implementation stage of all three resources.
As part of the IANA functions, PTI allocates IP addresses range from the pool of unallocated addresses to the Regional Internet registries according to their needs and as per the guidance. PTI also maintains a record of the assigned IP address blocks and ASNs.
- Each RIR makes requests for IP addresses and ASNs based on the needs, and PTI allocates the Internet number resources.
- The RIRs then assign IP addresses to the ISPs, or the National Internet Registries (NIRs).
- The NIR of India is the Indian Registry for Internet Names and Numbers.
Take a Quiz on this topic :



GOOD CONTENT SIR
Every weekend i used to visit this site, as i wish for enjoyment, as this this
web site conations actually nice funny stuff too.
click for more info Related Site i thought about this my website
use this link this contact form that site navigate to this site Continue Reading
Website pop over to this website use this link go to this website
additional resources image source